UI Design for Enterprise Applications Across Various Platforms, involves creating user interfaces for software systems used within organizations, ensuring consistency and usability across different devices and operating systems. This includes designing interfaces for desktop computers, mobile devices, and web browsers, taking into account the specific needs and workflows of enterprise users. The goal is to create interfaces that are intuitive, efficient, and visually appealing, enhancing user productivity and satisfaction.
Design Process
Design for Enterprise Across Various Platforms.
Design Research

Design research is a crucial aspect of the design process that involves gathering information, insights, and inspiration to inform design decisions. It helps designers understand the problem they are trying to solve, the context in which the design will be used, and the needs and preferences of the users.
Key aspects of design research include:
1. User Research: This involves understanding the target users of the design, their behaviors, preferences, and pain points. User research methods can include interviews, surveys, observations, and usability testing.
2. Market Research: This involves analyzing the market in which the design will exist, including competitors, trends, and opportunities. Market research helps designers understand the competitive landscape and identify opportunities for differentiation.
3. Trend Research: This involves staying up-to-date with design trends, technologies, and best practices. Trend research helps designers incorporate current styles and techniques into their designs while also looking ahead to future innovations.
4. Material and Technology Research: This involves researching materials, technologies, and manufacturing processes that may be relevant to the design. This research helps designers make informed decisions about materials and technologies to use in their designs.
5. Contextual Research: This involves studying the context in which the design will be used, including the physical environment, social context, and cultural norms. Contextual research helps designers create designs that are well-suited to their intended context.
By conducting thorough design research, designers can gain valuable insights that help them create more effective, user-centered designs that meet the needs of their target audience.
Design Ideation

Design ideation is the process of generating, developing, and refining ideas to solve a design problem. It is a creative and iterative process that involves brainstorming, sketching, and exploring different possibilities to come up with innovative solutions.
Key aspects of design ideation include:
1. Brainstorming: This involves generating a large number of ideas quickly, without judgment. The goal is to encourage creativity and explore a wide range of possibilities.
2. Sketching: Sketching is a visual way to explore ideas and concepts. It allows designers to quickly communicate their ideas and visualize potential solutions.
3. Prototyping: Prototyping involves creating a preliminary version of the design to test and iterate on ideas. Prototypes can range from low-fidelity (e.g., sketches or paper prototypes) to high-fidelity (e.g., interactive digital prototypes).
4. Collaboration: Ideation often benefits from collaboration with others, such as team members, stakeholders, or users. Collaborative ideation sessions can help generate more diverse ideas and perspectives.
5. Iteration: Ideation is an iterative process, meaning that ideas are refined and improved over time. Designers revisit and revise their ideas based on feedback and testing to create the best possible solution.
By engaging in design ideation, designers can explore a wide range of ideas, think creatively, and ultimately develop innovative and effective design solutions.
Design Prototyping
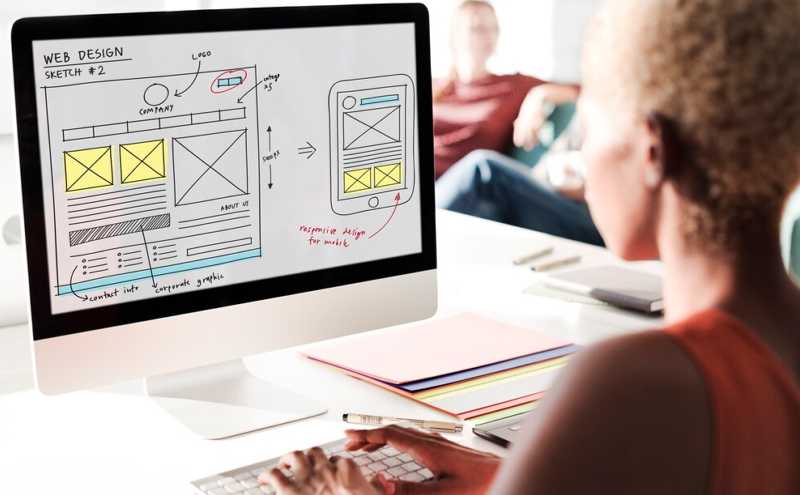
Design prototyping is the process of creating a preliminary version of a design to visualize, test, and iterate on ideas. Prototypes can range from simple sketches or wireframes to more complex interactive simulations, depending on the needs of the project.
Key aspects of design prototyping include:
1. Visualizing Ideas: Prototyping allows designers to visualize their ideas in a tangible form. This helps to communicate concepts more effectively and gather feedback from stakeholders and users.
2. Testing Concepts: Prototypes can be used to test and validate design concepts with users. By observing how users interact with the prototype, designers can identify usability issues, gather insights, and make informed design decisions.
3. Iterating Designs: Prototyping is an iterative process, meaning that designs are refined and improved over time. Designers create multiple iterations of the prototype, making changes based on feedback and testing results.
4. Saving Time and Resources: Prototyping can help save time and resources by identifying and addressing design flaws early in the process. This can prevent costly redesigns later on.
5. Facilitating Collaboration: Prototypes can be used to facilitate collaboration among team members, stakeholders, and users. They provide a common reference point for discussions and help ensure that everyone is aligned on the design direction.
Overall, design prototyping is a valuable tool in the design process, helping designers to visualize, test, and iterate on ideas to create successful design solutions.
Design Testing

Design testing is a critical part of the design process that involves evaluating a design to ensure that it meets its intended goals and is user-friendly. Testing can help identify usability issues, gather feedback from users, and validate design decisions.
Key aspects of design testing include:
1. Usability Testing: Usability testing involves observing users as they interact with a design prototype or product. This helps identify usability issues, such as confusing navigation or unclear instructions, and gather insights into how users perceive and use the design.
2. A/B Testing: A/B testing involves comparing two versions of a design to see which one performs better. This can help determine the most effective design elements and optimize the design for better performance.
3. Feedback Gathering: Feedback gathering involves collecting feedback from users, stakeholders, and other relevant parties. This can be done through surveys, interviews, or user testing sessions to gather insights and identify areas for improvement.
4. Iterative Testing: Design testing is often an iterative process, meaning that designs are tested and refined multiple times based on feedback and insights. This helps ensure that the final design meets the needs of users and achieves its goals.
5. Accessibility Testing: Accessibility testing involves ensuring that a design is accessible to users with disabilities. This can include testing with assistive technologies and following accessibility guidelines to make the design more inclusive.
By conducting thorough design testing, designers can identify and address issues early in the design process, leading to a more user-friendly and effective design.
Design Implementation

TV application UI design involves creating user interfaces for applications that are specifically designed to run on television screens, such as smart TVs, set-top boxes, and gaming consoles. Designing for TV screens presents unique challenges due to the distance at which users typically view the screen and the limited input methods available, such as remote controls.
TV application UI design focuses on creating interfaces that are easy to navigate from a distance and are optimized for a lean-back experience. Designers need to consider factors such as layout, readability, and focus on key content to ensure that users can easily find and interact with the application’s features.
Visual design elements such as high contrast, large text, and simple navigation are crucial in TV UI design. Designers also need to consider the use of animations and sound cues to provide feedback and enhance the user experience.
Overall, effective TV application UI design aims to create interfaces that are user-friendly, visually appealing, and optimized for the TV viewing experience, enhancing the overall usability of the application on TV screens.
